

Right after modifying/added files it would show us the list of untracked files and files that are tracked. You have the option of either stage them and commit them to your repository, or remove them!
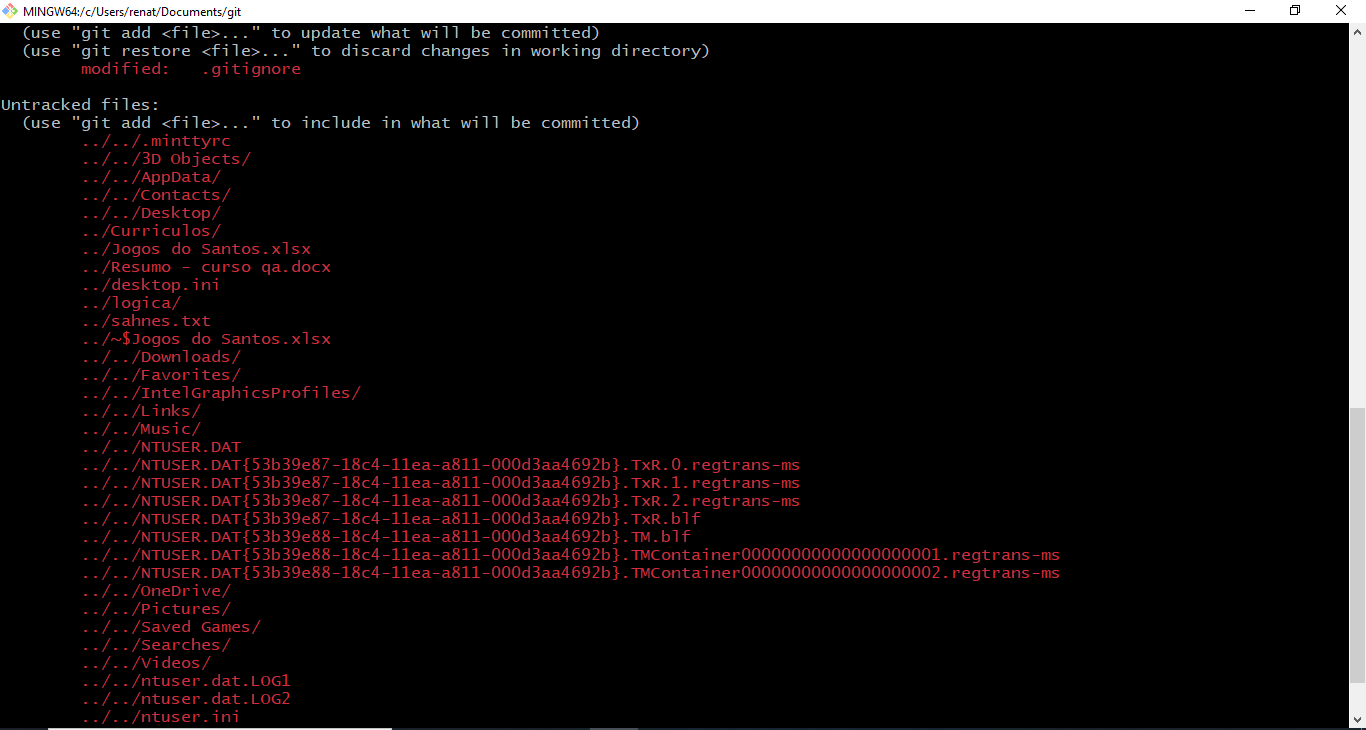
Means those files added and committed in a previous snapshot and that Git is aware, tracking them for changes.įiles are the opposite, those files were not in the previous commit and have not been staged to be committed. In your working or local directory your files are either tracked or untracked. We’ll refer to a few examples so you can get started quickly.ĭifference Between Tracked vs.
#Git status ignore untracked how to#
In this guide, we’re going to discuss how to remove untracked files with Git. The git clean -fd command, which removes untracked files and directories The git clean -fx command, which removes untracked and tracked files gitignore file, which ignores the files and directories in a repository There are leftover files from other merges, or you want to remove certain files.Ī. You pointed Git to a folder you didn’t want to Our working (local) directory cluttered by unused files , and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email. Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your EmployerĬareer Karma matches you with top tech bootcampsĪccess exclusive scholarships and prep courses.Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps.Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants.Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans.
#Git status ignore untracked free#

I actually have the SVN checkout and the Git clone both sitting in the same directory. I’ve found a lot of value in using GitHub for reviewing and collaborating on patches via pull requests. While working on patches in a fork, however, Git is definitely for better. Over several years now I’ve used Git in developing patches for WordPress core, for which we committers still use SVN to actually commit patches, for better or worse.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
